 The AT&T Biconic
AT&T named their first commercial fiber optic connector the “Biconic” since the connector had a conical molded-plastic ferrule that fitted into a “bi-conical” mating adapter when connected to another connector. The original Biconic was actually molded around the fibers to get exact centering, a practice that stopped when they developed a way to insert a 125 micron ( 5 mil) pin in the plastic molding cavity to produce a connector ferrule with a hole into which fibers could be epoxied.
The AT&T Biconic
AT&T named their first commercial fiber optic connector the “Biconic” since the connector had a conical molded-plastic ferrule that fitted into a “bi-conical” mating adapter when connected to another connector. The original Biconic was actually molded around the fibers to get exact centering, a practice that stopped when they developed a way to insert a 125 micron ( 5 mil) pin in the plastic molding cavity to produce a connector ferrule with a hole into which fibers could be epoxied.
 SMA
The SMA connector was the first connector widely used for data links using multimode fiber. It was developed by Amphenol using the hardware from the “SubMiniature A” microwave connector, hence it’s name, with a precise 1/8 inch machined metal ferrule.
The next major development in fiber optic connectors came from Japan, with the development of the ceramic ferrule. Metal ferrules had a problem with glass fiber. The uneven expansion coefficients sometimes caused the adhesive to fail, allowing the fiber to extend or retract, a process called “pistoning.” The ceramic ferrule had a very low expansion, like glass, so the adhesive held better, the connector could be polished to a finer finish and performed better over extremes in temperature.
SMA
The SMA connector was the first connector widely used for data links using multimode fiber. It was developed by Amphenol using the hardware from the “SubMiniature A” microwave connector, hence it’s name, with a precise 1/8 inch machined metal ferrule.
The next major development in fiber optic connectors came from Japan, with the development of the ceramic ferrule. Metal ferrules had a problem with glass fiber. The uneven expansion coefficients sometimes caused the adhesive to fail, allowing the fiber to extend or retract, a process called “pistoning.” The ceramic ferrule had a very low expansion, like glass, so the adhesive held better, the connector could be polished to a finer finish and performed better over extremes in temperature.
 NTT FC
NTT FC  AT&T ST
The “FC” or “fiber connector” from NTT (Nippon Telephone and Telegraph) was the first connector to use the 2.5 mm ceramic ferrule. Shortly thereafter, AT&T introduced the “ST” or “straight terminus” that used exactly the same ceramic ferrule as the FC but replaced the screw-on nut of the FC with a bayonet lock like a BMC coax connector, simplifying and speeding up connector insertion. NTT responded a couple of years later with the “SC” or “subscriber connector” and the ST and SC dominated fiber optics for over a decade. The 2.5 mm ferrule was also used in the FDDI and ESCON connectors, both named for the systems for which they were designed.
AT&T ST
The “FC” or “fiber connector” from NTT (Nippon Telephone and Telegraph) was the first connector to use the 2.5 mm ceramic ferrule. Shortly thereafter, AT&T introduced the “ST” or “straight terminus” that used exactly the same ceramic ferrule as the FC but replaced the screw-on nut of the FC with a bayonet lock like a BMC coax connector, simplifying and speeding up connector insertion. NTT responded a couple of years later with the “SC” or “subscriber connector” and the ST and SC dominated fiber optics for over a decade. The 2.5 mm ferrule was also used in the FDDI and ESCON connectors, both named for the systems for which they were designed.
 FDDI
FDDI  IBM ESCON
The next confusing nomenclature for fiber optic connectors came from the polishing of the end of the ferrule, giving us “PC,” “Ultra PC” or “Super PC” and “APC” connectors. As the long-haul industry moved from multimode (MM) to singlemode (SM) fiber around 20 years ago, the reflections at SM connections caused big problems with most laser sources. The reflections actually interacted with the lasers, causing instability and noise in the laser itself.
Early connectors like the biconic and SMA, which did not have keyed ferrules and could rotate in mating adapters, always had an air gap between the connectors to prevent them rotating and grinding scratches into the ends of the fibers. The air gap between the fibers causes a reflection when the light encounters the change in refractive index from the glass fiber to air in the gap.
IBM ESCON
The next confusing nomenclature for fiber optic connectors came from the polishing of the end of the ferrule, giving us “PC,” “Ultra PC” or “Super PC” and “APC” connectors. As the long-haul industry moved from multimode (MM) to singlemode (SM) fiber around 20 years ago, the reflections at SM connections caused big problems with most laser sources. The reflections actually interacted with the lasers, causing instability and noise in the laser itself.
Early connectors like the biconic and SMA, which did not have keyed ferrules and could rotate in mating adapters, always had an air gap between the connectors to prevent them rotating and grinding scratches into the ends of the fibers. The air gap between the fibers causes a reflection when the light encounters the change in refractive index from the glass fiber to air in the gap.
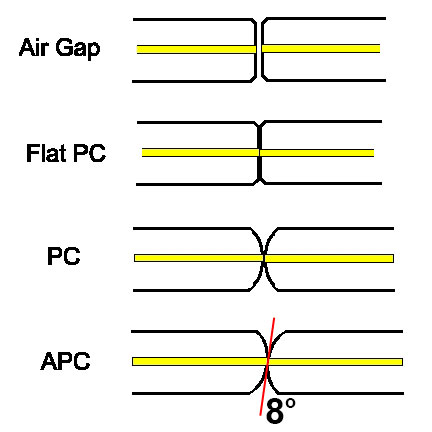 Beginning with the ST and FC, which had keyed ferrules, connectors were designed to contact mating ferrules tightly, creating what we now call “PC” or “physical contact” connectors. Reducing the air gap reduced both loss and back reflection, since light has a loss of about 5% (~0.25 dB) at each air gap. While air gap connectors usually had losses of 0.5 dB or more and return loss of 20 dB (1%), PC connectors had typical losses of 0.3 dB and a return loss of 30 to 50 dB (0.1 to 0.001%.)
Connectors use a number of polishing techniques to create a convex end to the connector ferrule to insure physical contact of the fiber ends. Hand polishing is done on a rubber pad and machine polishing uses concave polishing fixtures. “Super PC” or “Ultra PC” are simply marketing names various manufacturers give to their polishing processes.
The final solution for singlemode systems extremely sensitive to reflections, like CATV or high bitrate telco links, was to angle the end of the ferrule 8 degrees to create what we call an “APC” or “angled PC” connector. Then any reflected light is at an angle that is absorbed in the cladding of the fiber.
It seems like more recent connectors, like the “SFF” or “small form factor” connectors were named by the marketing department instead of engineering, which is why we have names like “Volition” and “OptiJack.” But the exception is the "LC" or lightwave connector, “MT” (“mass termination” or "multiple termination") for 12 or 24 fibers (also called MTP "multiple termination push-on" or MPO - "multi-fiber push-on") and its duplex cousin, the “MT-RJ” where “RJ” refers to the “RJ-45” style of copper connector.
Beginning with the ST and FC, which had keyed ferrules, connectors were designed to contact mating ferrules tightly, creating what we now call “PC” or “physical contact” connectors. Reducing the air gap reduced both loss and back reflection, since light has a loss of about 5% (~0.25 dB) at each air gap. While air gap connectors usually had losses of 0.5 dB or more and return loss of 20 dB (1%), PC connectors had typical losses of 0.3 dB and a return loss of 30 to 50 dB (0.1 to 0.001%.)
Connectors use a number of polishing techniques to create a convex end to the connector ferrule to insure physical contact of the fiber ends. Hand polishing is done on a rubber pad and machine polishing uses concave polishing fixtures. “Super PC” or “Ultra PC” are simply marketing names various manufacturers give to their polishing processes.
The final solution for singlemode systems extremely sensitive to reflections, like CATV or high bitrate telco links, was to angle the end of the ferrule 8 degrees to create what we call an “APC” or “angled PC” connector. Then any reflected light is at an angle that is absorbed in the cladding of the fiber.
It seems like more recent connectors, like the “SFF” or “small form factor” connectors were named by the marketing department instead of engineering, which is why we have names like “Volition” and “OptiJack.” But the exception is the "LC" or lightwave connector, “MT” (“mass termination” or "multiple termination") for 12 or 24 fibers (also called MTP "multiple termination push-on" or MPO - "multi-fiber push-on") and its duplex cousin, the “MT-RJ” where “RJ” refers to the “RJ-45” style of copper connector.
 AT&T LC
AT&T LC
 MTP
MTP  MT-RJ
MT-RJ
Note: The article is from The Fiber Optic Association www.thefoa.org, edited by Elena.


 SMA
SMA NTT FC
NTT FC  AT&T ST
AT&T ST FDDI
FDDI  IBM ESCON
IBM ESCON
 AT&T LC
AT&T LC MTP
MTP  MT-RJ
MT-RJ